After the Ballots
How the ‘year of elections’ reshaped treasury priorities
Published: January 01, 1999

Over the last 5 years, extensive efforts have been made to encourage electronic payment methods over cheques. Improvements in channels coverage; such as Mobile Money or Near-field communication, and cost; such as Automated clearing house for bulk clearing, had seen the cost of electronic transacting reduce significantly. Though reductions in Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) and Consumer-to-Business cheque usage have been encouraging, the Business-to-Business and Business-to-Consumer space is still heavily dependent on the issuance of cheques for a variety of reasons.
This article suggests ways that businesses can manage the cost of cheque processing and mitigate fraud risk.
Over the last 5 years, the payment industry has increasingly embraced paperless and automated solutions. As a result, the relative importance of cheques has decreased in many countries, prompting experts and authorities in some countries to predict and act to accelerate the demise of cheque payments. However, cheques continue to be extensively used.
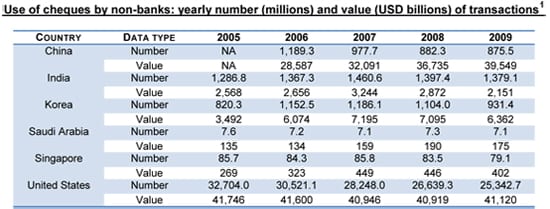
[1] Statistics on payment and settlement systems in the CPSS countries - Figures for 2009, Bank for International Settlements (BIS), March 2011
Data collated by the Bank of International settlement shows a significant reduction in cheque usage. But the increase in value suggests that the issued value of each cheque continues to be high, which can be attributed to consumers adopting electronic payment methods.
This indicates a large residual user base such as businesses that are still reliant on cheques for payments and collections. There are many reasons for the continued use of cheques. With advances in electronic payment methods, these reasons will become less and less relevant. But until then, reasons for their usage continue to be compelling.

Chart 1. Reasons for not switching to electronic payment methods for different payment flows
Treasurers face high costs of switching from cheques to electronic payment methods. The various legacy systems and processes require intensive investment in technology and operations. In many cases, this investment will not be forthcoming for a variety of reasons including the current economic environment.[[[PAGE]]]
Options for streamlining the cheque issuance process
What can treasurers do to lower their cost of payment processing? One of the many ways of lowering the cost of manual cheque payment issuance is through outsourcing of the cheque issuance process. The two main approaches that treasurers can take to outsource their cheque issuance process are consolidation and dissemination. Both these models give treasurers the ability to centralise process risks and controls, but provide different propositions based on business requirement.

Diagram 1. Consolidation vs. Dissemination cheque issuance approach

Chart 2. Summary of key facts for cheque issuance process
In the consolidated approach (chart 2), the cheque is printed and delivered by the bank upon instruction from treasurers. Whereas in the disseminated approach, the cheque is processed electronically by the bank, but the printing is instead done at client premises via MICR-enabled printers. Both of these approaches offer benefits and features that can help streamline the cheque issuance process for the company.
Adoption of the consolidated or disseminated approach is dependent on cheque payment requirements; such as speed of issuance, approval process, and cost. The treasurer should select a bank provider who is able to provide the flexibility for the client to implement a hybrid solution. This allows the treasurer to prioritise urgent and sensitive cheque payments through the disseminated model; and non-urgent payments via the outsourced route.[[[PAGE]]]
Based on our experience with the disseminated model, clients who use this service need a fast turnaround time to issue payments to their beneficiaries with centralised approval. In the consolidated approach, however, clients tend to make regular payments such as dividends, payroll that is predictable and not time-sensitive.
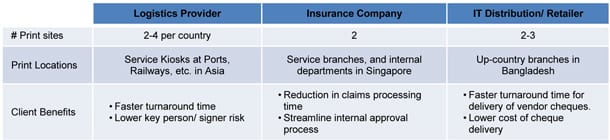
Chart 3. Use Cases for Onsite Cheque Printing
In both of these approaches, cheque fraud risk is present; especially in the emerging markets, where this risk remains high. Mitigants include better security of cheque books/stationery, robust reconciliation process and anti-fraud cheque stationery. These are passive fraud prevention methods that a treasurer can employ in their cheque issuance processes.
A good way to actively monitor and manage the cheque prevention process is the use of Positive pay. This service is widely used in the Americas, but is seldom offered by bank providers in emerging markets. Positive pay is essentially a simple service that matches Cheque issuance information provided by the issuer, with cheque details provided by the clearing house. Any mismatches will be flagged and exception handling will be dependent on customisable rules set by the corporate treasury that issues the cheques.
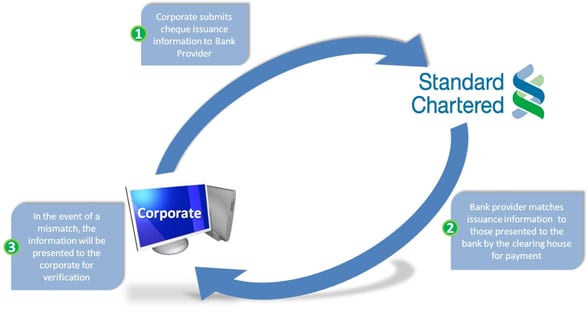
This fraud prevention tool is highly effective in addition to the security features available on the bank providers’ cheque stationery.[[[PAGE]]]
For the corporate treasurer looking to streamline their cheque issuance process, here is a summary of some considerations to be made.
I. Strategy
• Can I convince my beneficiaries to go electronic so I can pay them via electronic payment methods?
• Are my internal platforms and systems geared towards electronic payment?
At its root, electronic payment methods still provide the most efficient and cost effective method to make payment to your beneficiaries. So only consider cheque outsourcing if your company is unable to switch to electronic, but with a desire to streamline its cheque issuance process.
II. Requirement and Needs
• Does the number of cheques that need to be issued justify outsourcing of my process to a bank provider?
• How fast do my beneficiaries expect these cheque payments to be made?
Understanding your own needs allows the corporate treasury to make a more informed decision. This allows the treasurer to select the outsourcing approach that is most suitable for the company’s account payables operations. Selection of the right approach to implement cheque outsourcing is most important in determining the return on investments put into the implementation of the cheque outsourcing initiative.
III. Selection Criteria
• Does the bank provider have direct access to the clearing system?
• Can the bank provider provide me with tools such as reconciliation reports, cheque customisation, fraud prevention and faster issuance?
Finally, the corporate treasury needs to ensure that the bank provider who is handling your outsourced cheque issuance process has the necessary experience, access and tools to help your company maximise the returns from outsourcing.
Cheques continue to be a popular form of payment due to a variety of reasons, and will remain so in the short to medium term. This is especially so for emerging markets in Asia, Africa and the Middle East that we suspect will in time gear towards establishing a full-fledged electronic payment economy.
One effective method of managing this cumbersome payment method is to outsource the corporate cheque issuance process through close partnership with a bank provider. This bank provider should understand corporate requirements and help to deliver savings, risk mitigation and better control and governance processes to justify the cost of implementing the outsourcing arrangement.
Excellence in this area for the corporate treasury will not only provide cost savings & reduce risk, but also present opportunities to streamline existing processes for greater efficiency to focus on core activities.